The lateral folding (in the transversal direction, rolling up)
Introduction
- The lateral folding in the transversal direction (rolling up)
- The cephalo-caudal folding longitudinal direction)
- Comparison of the two foldings
At the same time as the cephalo-caudal flexion a lateral folding occurs in the initially still flat embryo. This folding results in an enclosure of the endoderm by the ectoderm.
In order to make it easier to understand this lateral folding, this process can be divided into two steps.
- In a first step the laterally lying structures, due to the large and rapid growth of the internal embryonic anlage (especially due to the disintegration of the somites), are shoved in a ventral direction.
Some of the structures lying in the middle are then pressed against each other and fuse. This is true for the pair of preformed aortae dorsales (stage 12), which thus become the aorta mediana, and for the medial section of the splanchnopleura that forms the dorsal mesenterium. - The second step of the lateral folding has to do with the endoderm, from which the inner covering of the gastro-intestinal tract arises.
The ectoderm of the caudal and cephalic ends of the embryo coalesce, due to the ventral folding along a medial line. During this process of folding the amnion is pulled by the ectoderm. Out of the small, dorsally-lying amniotic cavity a large one is thus created that surrounds the whole embryo and presses closely on the body stalk and the yolk sac. This is how the umbilical cord is formed.
The endoderm, which becomes closed at both ends as well as along the side of the embryo, forms a tube (future for-, mid- and hindgut).
In the beginning (stage 9) the midgut stands in an open connection to the umbilical vesicle (yolk sac) and the allantois. Both structures later atrophy and are taken up in the umbilical cord. The connection between the embryo and extraembryonic appending organs remains up to the time of delivery, in order to permit the passage of the vital umbilical vessels which are located in the umbilical cord (stage 12).
The intraembryonic coelom, a cavity between the splanchnopleura mesoderm (outer covering of the intestines) and the somatopleura mesoderm (inner covering of the trunk wall), which in the beginning is connected with the extraembryonic coelom (= chorionic cavity!), becomes separated from it by the folding and fusion of the lateral sides of the embryo. The intraembryonic coelom ring is formed.
- Cephalo-caudal flexion takes place in the A plane
- Lateral folding takes place in the C plane

In order to understand the process of folding better (after stage 9), the forgoing stages are also depicted.
The gray elements are only visible on the longitudinal section. This is shown on the previous page.
- 1
- Amniotic cavity
- 2
- Ectoderm
- 3
- Umbilical vesicle
- 4a
- Endoderm
- 4b
- Endoderm that joins together
again under the notochorde - 4c
- Completely joined up endoblast
- 5
- Body stalk
- 6a
- Allantois
- 6b
- Lengthened allantois
- 7
- Extraembryonic mesoderm
- 8
- Cloacal membrane
- 9
- Notochordal process
- 10a
- Primitive streak
- 10b
- Shrinking Primitive streak
- 11a
- Neural plate
- 11b
- Neural folds
- 12
- Central axial canal
- 13
- Primitive node
- 14a
- Ventrally merged
notochord - 14b
- Ventrally resorbed
notochord - 14c
- Free notochord
- 15
- Prechordal plate
- 16
- Canalis neurentericus
- 17
- Pharyngeal membrane
- 18
- Cardiac plate
- 19
- Pericardial space
- 20
- Fused neural tube
- 21
- Septum transversum
- 22
- Closure of the anterior neuroporus
- 23
- Caudal recessus
- 24
- Thyroid gland anlage
- 25
- Lung anlage
- 26
- Liver anlage
- 27
- Closure of the posterior neuroporus
- 28
- Dorsal aorta
- 29
- Aortae
- 30
- Umbilical veins
- 31
- Intraembryonic mesoderm
- 32
- Paraxial mesoderm
- 33
- Intermediate mesoderm
- 34
- Lateral plate mesoderm
- 35
- Somitocoel
- 36
- Somite
- 37
- Nephrogenic cord

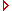 Stage 6 (17th day)
Stage 6 (17th day)










