Blood supply of the liver
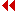
The blood supply of the liver has two sources: on the one hand the hepatic artery (oxygenated), a branch of the coeliac artery, and on the other the venous blood of the entire region of the intestines collected by the portal vein. This last circulation is rich in nutrients.and first pass through the liver on its way to the inferior vena cava.

- 1
- Venous sinus
- 2
- Superior cardinal vein
- 3
- Inferior cardinal vein
- 4
- Left common cardinal vein
- 5
- Right umbilical vein
- 6
- Liver
- 7
- Anastomosis between left and right omphalomesenteric vein
- 8
- Right umbilical vein (prehepatic)
- 9
- Left umbilical vein
- 10a
- Right omphalomesenteric vein
- 10b
- Left omphalomesenteric vein
- 11
- Umbilical veins (unpaired)
- 12
- Inferior vena cava
- 13
- Venous duct
- 14
- Portal vein
- 15
- Splenic vein
- 16
- Ductus choledochus
- 17
- Dorsal pancreas
- 18
- Ventral pancreas
- 19
- Minor duodenal papilla
- 20
- Major duodenal papilla
The liver acini are arranged around the capillary region of the omphalomesenteric vein.
A part of the umbilical vein also gets into the liver and anastomoses with this capillary region.

- 1
- Venous sinus
- 2
- Superior cardinal vein
- 3
- Inferior cardinal vein
- 4
- Left common cardinal vein
- 5
- Right umbilical vein
- 6
- Liver
- 7
- Anastomosis between left and right omphalomesenteric vein
- 8
- Right umbilical vein (prehepatic)
- 9
- Left umbilical vein
- 10a
- Right omphalomesenteric vein
- 10b
- Left omphalomesenteric vein
- 11
- Umbilical veins (unpaired)
- 12
- Inferior vena cava
- 13
- Venous duct
- 14
- Portal vein
- 15
- Splenic vein
- 16
- Ductus choledochus
- 17
- Dorsal pancreas
- 18
- Ventral pancreas
- 19
- Minor duodenal papilla
- 20
- Major duodenal papilla
The two branches of the umbilical vein, which empty directly into the venous sinus, atrophy. All of the placental blood goes into the liver capillary region.
Within the liver a direct connection forms, the venous duct, which goes around the capillary region. This functions as an important blood pressure regulator.
Transverse anastomoses form between the left and right omphalomesenteric veins around the duodenum below the liver.

- 1
- Venous sinus
- 2
- Superior cardinal vein
- 3
- Inferior cardinal vein
- 4
- Left common cardinal vein
- 5
- Right umbilical vein
- 6
- Liver
- 7
- Anastomosis between left and right omphalomesenteric vein
- 8
- Right umbilical vein (prehepatic)
- 9
- Left umbilical vein
- 10a
- Right omphalomesenteric vein
- 10b
- Left omphalomesenteric vein
- 11
- Umbilical veins (unpaired)
- 12
- Inferior vena cava
- 13
- Venous duct
- 14
- Portal vein
- 15
- Splenic vein
- 16
- Ductus choledochus
- 17
- Dorsal pancreas
- 18
- Ventral pancreas
- 19
- Minor duodenal papilla
- 20
- Major duodenal papilla
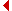
In this stage the right umbilical vein as well as a part of the omphalomesenteric vein atrophy.
Through the atrophy of the left sinus horn the left outflow of the omphalomesenteric vein also involutes.

- 1
- Venous sinus
- 2
- Superior cardinal vein
- 3
- Inferior cardinal vein
- 4
- Left common cardinal vein
- 5
- Right umbilical vein
- 6
- Liver
- 7
- Anastomosis between left and right omphalomesenteric vein
- 8
- Right umbilical vein (prehepatic)
- 9
- Left umbilical vein
- 10a
- Right omphalomesenteric vein
- 10b
- Left omphalomesenteric vein
- 11
- Umbilical veins (unpaired)
- 12
- Inferior vena cava
- 13
- Venous duct
- 14
- Portal vein
- 15
- Splenic vein
- 16
- Ductus choledochus
- 17
- Dorsal pancreas
- 18
- Ventral pancreas
- 19
- Minor duodenal papilla
- 20
- Major duodenal papilla
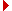
Through various structural altering processes of the venous side arises the inferior vena cava, which behind the liver empties into the right atrium.
Blood from the left umbilical vein, branches of the omphalomesenteric vein and the splenic vein flow into the liver.
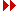
Following birth the flow from the placental blood circulation system dries up (left umbilical vein).