|

|
|
|
|
Schematically, three implantation stages can be distinguished:·
- Adplantation of the blastocyst on the endometrium
- Adhesion of the blastocyst to the endometrium
- Invasion of the trophoblast and embedding
|
|
|
|
Adplantation of the blastocyst on the uterine mucosa
|
|
|
The adhesion can occur when beforehand the uterus has entered its secretory phase (luteinizing phase). This reception-ready phase of the endometrium lasts 4 days (20th -23rd day) and is usually termed the "implantation window". It follows around 6 days after the LH peak and is characterized by the appearance of small elevations at the apical pole of the epithelial endometrium cells. One of the tasks of these elevations consists in the absorption of the uterine fluid, which brings the blastocyst nearer to the endometrium and immobilizes it at the same time. In this stage the blastocyst can still be eliminated by being flushed out. There is also a hypothesis that the progesterone and the oestrogen are responsible for an oedema that already fills the flattened out uterine cavity. This is also supposed to contribute to the blastocyst being pressed against the uterine epithelium 4.
|
|
|
| Fig. 16 - Implantation window |
|
Legend |
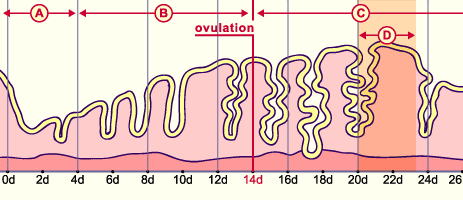
A
B
C
D |
Menstruation
Proliferation
Secretion
Implantation window |
|
|
|
Fig. 16
Menstruation cycle with the cyclic alterations of the endometrium. The "implantation window" that corresponds to the period of maximum receptivity is depicted here (D).
|
|
More info
|
|
Pellucid zone
During the whole time span from ovulation up to implantation, the oocyte is enveloped by the pellucid zone, the role of which changes. Initially it is united with the cells of the corona radiata during the transport of the oocyte within the fallopian tube. At the moment of fertilization it facilitates the acrosomal reaction of the sperm cells. Finally, after the cortical reaction has taken place, it undergoes physical and chemical changes. The pellucid zone possesses no HLA antigen and thus acts as an immunological barrier in relation to the mother. Another important role is the prevention of a premature implantation of the embryo in the tube region.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Adhesion of the blastocyst to the endometrium
|
|
|
|

