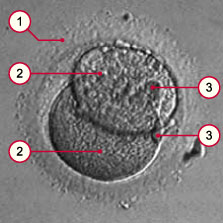
1
2
3
|
Pellucid zone
Blastomere (cleavage cell)
Polar bodies |
|
|
|
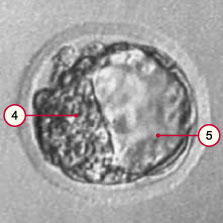
4
5 |
Inner collection of cells
(embryoblast)
Blastocyst cavity |
|
|
|
Fig. 1
A two-cell embryo has been created through the division of the zygote. Picture made roughly 24 hours after the in-vitro fertilization
Fig. 2
This form of the embryo is called a blastocyst because the cells enclose a fluid-filled cavity on the inside. On the fifth day after fertilization
© Dr. A. Senn et al, CHUV Lausanne
|

