|

|
|
|
20.1 Formation of the urinary organs
|
|
|
Development of the urinary organs (3rd - 4th week)
|
|
|
|
The development of the urinary system is closely related to that of the genital system which will be described, though, in a separate module. The urinary organs consist of the kidneys (which produce urine, among other things), the ureter (transport of the urine from the kidneys to the bladder), the bladder (temporary storage for the urine) and the urethra (transport of the urine from the bladder to the external world).
In all vertebrates the kidneys and ureters develop out of the intermediate mesoderm, whereas bladder and urethra derive from the urogenital sinus.
|
|
|
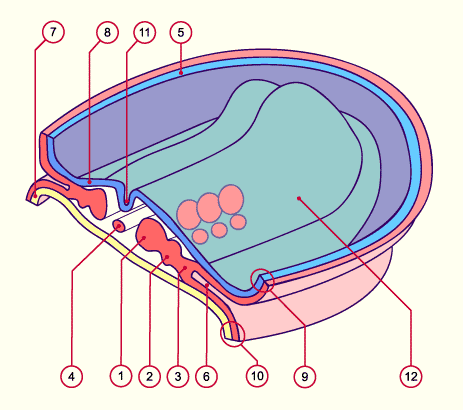
Fig. 1 - Transverse section and dorsal view of an embryo (trilaminar)
(ca. 21 days) |
|
Legend |
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12 |
Paraxial mesoderm
Intermediate mesoderm
Lateral mesoderm
Notochord
Amnion
Intraembryonic coelom
Endoderm
Ectoderm
Somatopleural (mesoderm and ectoderm)
Splanchnopleural (mesoderm and endoderm)
Neural groove
Neural ridge |
|
|
|
Fig. 1
Schematic diagram: Transverse section (in the midcephalic region) with a dorsal view of the three-
layered embryo towards the end of the 3rd week of development. The intermediate mesoderm lies between the somites (paraxial mesoderm) and the lateral mesoderm (out of which the coelom arises).
|
|
Due to the lateral folding, the intermediate mesoderm is shifted ventrally and loses its connection with the somites and the lateral mesoderm.
|
|
|
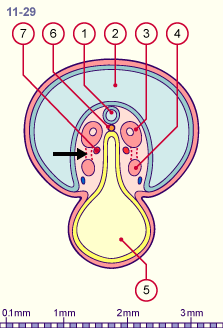
| Fig. 3 - Isolation of the nephrogenic cord (stage 11) |
|
Fig. 4 - Isolation of the nephrogenic cord (stage 12) |
|
Legend |
1
2
3
4
|
Neural tube
Amniotic cavity
Dermatomyome
Nephrogenic cord that has moved away from the paraxial mesoderm (somite) (black arrow) |
|
|
|
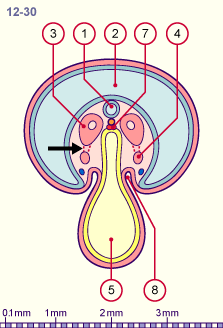
5
6
7
8 |
Yolk sac (umbilical vesicle)
Notochord
Aorta
Intraembryonic coelom |
|
|
|
Fig. 3, Fig. 4
The intermediate mesoderm moves ventrally and loses its connection (black arrow) to the somites and the lateral mesoderm. Also observe its approach towards the intraembryonic coelom.
|
|
|

