
1
2
3
|
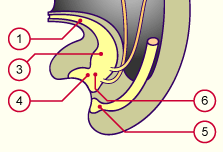
Allantois
Cloaca
Urinary bladder |
|
|
|
4
5
6 |
Phallic part of the definitive urogenital sinus
Rectum
Pelvic part of the definitive urogenital sinus |
|
|
|
Fig. 39
The cloaca subdivides. Observe that the metanephros in this stage still lies quite caudally.
Fig. 40
The uro-rectal septum has subdivided the cloaca into the primary urogenital sinus (ventrally) and the rectum (dorsally).
Out of the primary urogenital sinus arise the urinary bladder and the definitive urogenital sinus.
|

